Anonymization
Anonymization is a type of information sanitization whose intent is privacy protection. It is a data processing technique that removes or modifies personally identifiable information.
The below-mentioned transforms are available under the Dates category:
Data Hashing
Data Hashing is a technique of using an algorithm to map data of any size to a fixed length. Every hash value is unique.
Data Hashing is a data transformation technique used to convert raw data into a fixed-length representation in the form of a hash value. This transformation is often employed as part of the data preprocessing stage before using the data for various purposes such as analysis, machine learning, or storage. The main objective of data hashing as a data transform is to provide a more efficient and secure way to handle and process sensitive or large datasets.
Check out the given illustration on how to use Data Hashing transform.
Steps to perform the Anonymization Transform:
Navigate to a dataset within the Data Preparation framework, and select a column.
Select one column that needs to be protected.
Select the Transforms tab.
Select the Data Hashing transform from the Anonymization category.

The Data Hasing window opens.
Use the drop-down menu to get the available hashing options.

Select a Hash option (E.g., Sha2 hash option has been selected).
Set the Hash Value using the drop-down menu. The default Hash Value is 256 for the Sha2 hash option.
Click the Submit option.

Data in the selected column will be transformed using the hashed format.

Please Note:
A suitable hashing algorithm is chosen based on the specific requirements and security considerations as Hash Options. The supported Hash options are Hash, Sha-1, Sha-2, and MD-5.

The hash options displayed in the UI map to the following actual hashing algorithms on the backend:
Sha1 (UI) → SHA-256 (Backend)
Sha2 (UI) → SHA-512 (Backend)
Hash (UI) → MD-5 (Backend)
MD5 (UI) → MD-5 (Backend)
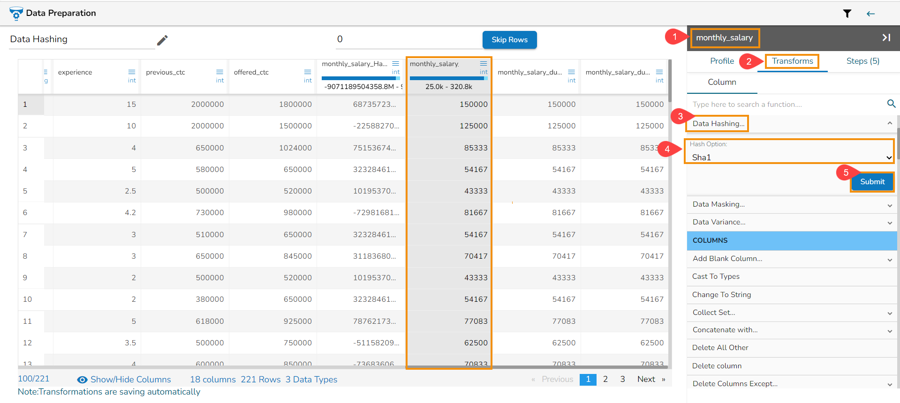
Data Hashing with Sha1 Hash Option
Select a column from the given dataset within the Data Preparation framework.
Open the Transforms tab.
Select the Data Hashing transform from the ANONYMIZATION category.
Select a column from data grid for transformation.
Select Sha1 as Hash Option.
Click the Submit option.
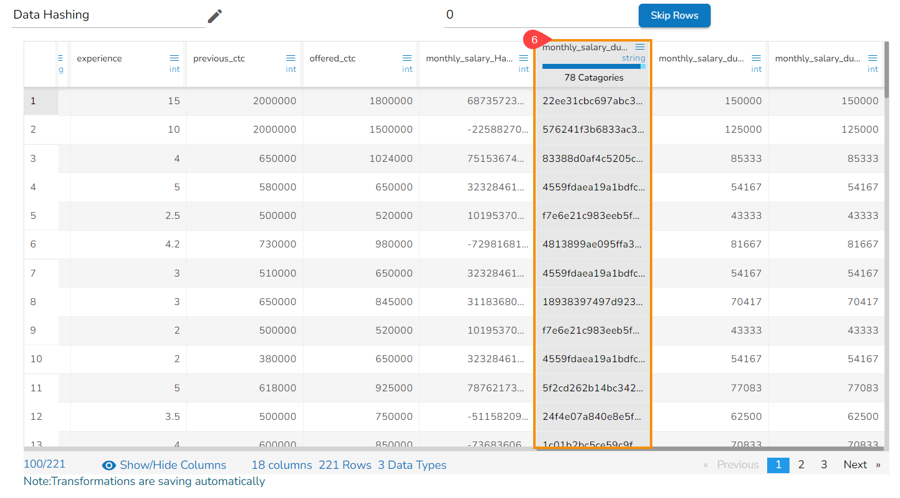
The selected column gets converted based on the hashing option.
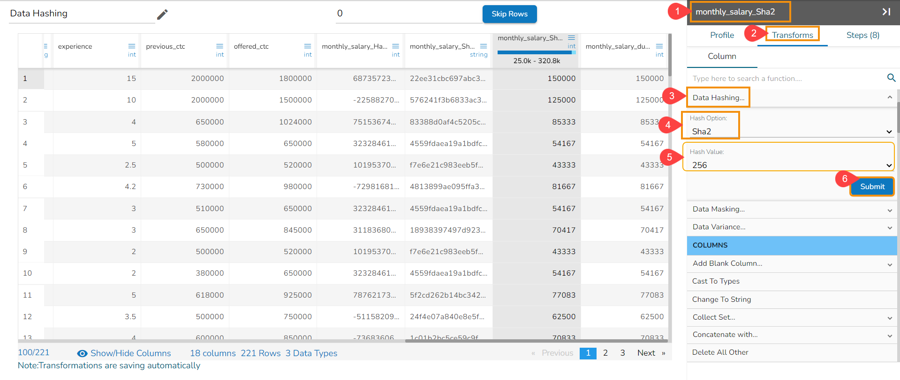
Data Hashing with Sha2 Hash Option
Select a column from the given dataset within the Data Preparation framework.
Open the Transforms tab.
Select the Data Hashing transform from the ANONYMIZATION category.
Select a column from data grid for transformation.
Select Sha2 as Hash Option.
Select a Hash Value from the drop-down (The supported values are 256, 384, and 512).
Click the Submit option.
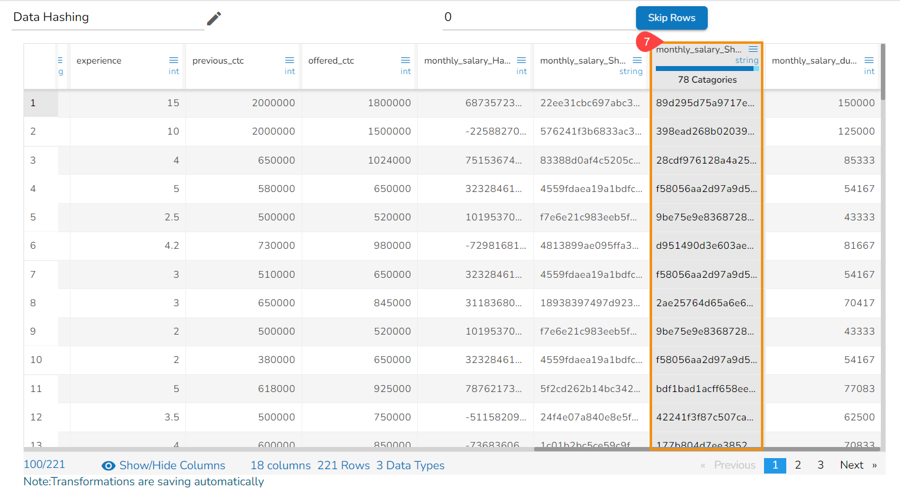
The selected column gets converted based on the hashing option.
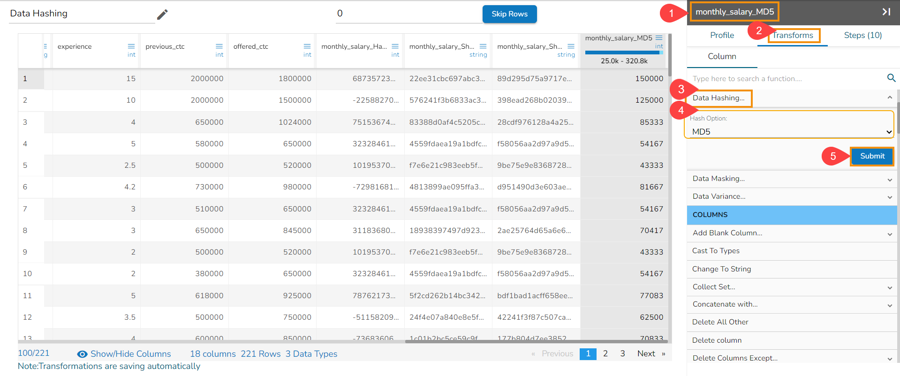
Data Hashing with MD5 Hash Option
Select a column from the given dataset within the Data Preparation framework.
Open the Transforms tab.
Select the Data Hashing transform from the ANONYMIZATION category.
Select a column from data grid for transformation.
Select MD5 as Hash Option.
Click the Submit option.
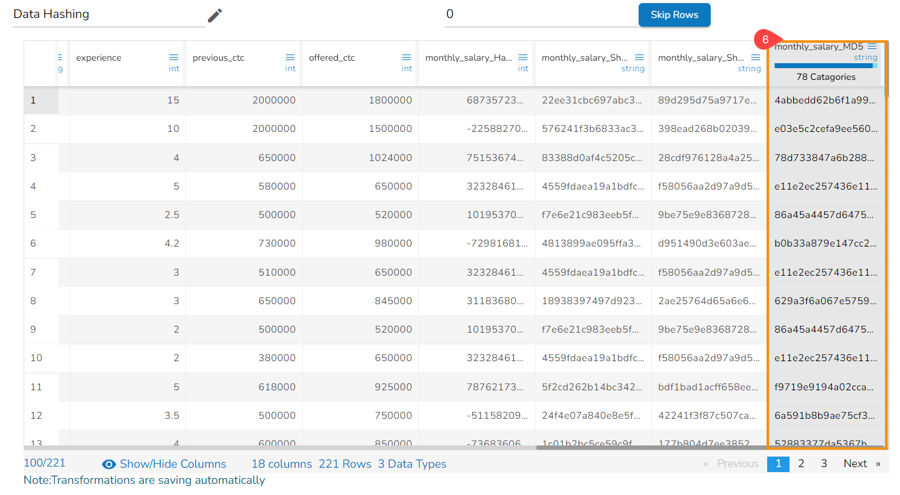
The selected column gets converted based on the hashing option.
Data Masking
Data masking transform is the process of hiding original data with modified content. It is a method of creating a structurally similar but inauthentic version of actual data.
Check out the given walk-through on the Data Masking transform.
Steps to perform the Data Masking Transform:
Navigate to a dataset within the Data Preparation framework, and select a column.
Select one column that needs to be protected.
Select the Transforms tab.
Select the Data Masking transform from the Anonymization category.

The Data Masking dialog box opens.
Provide the Start Index and End Index to mask the selected data.
Click the Submit option.

The image displays how the Data Masking transform (when applied to the selected dataset) converts the selected data:

Data Variance
The Data Variance transform allows the users to apply data variance to the Numeric and Date columns.
Applying the Data Variance transform to a Number Column
Check out the illustration on how to use the Data Variance on a numeric column.
Select a numeric column within the Data Preparation framework.
Open the Transforms tab.
Select the Data Variance transform from the Anonymization category.

The Data Variance dialog box opens.
Configure the following information:
Select Numeric as the Value Type.
Select an Operator using the drop-down option.
Set percentage.
Provide a comment in the given section.
Click the Submit option.

The data of the selected column gets transformed based on the set of numeric values.

Applying the Data Variance transform to a Date Column
Check out the illustration on how to use the Data Variance on a date column.
Select a column containing Date values from the given dataset within the Data Preparation framework.
Open the Transforms tab.
Select the Data Variance transform from the Anonymization category.

The Data Variance dialog box opens.
Configure the following information:
Select Date as the Value Type.
Select an Input Format from the drop-down list.
Select a Start Date using the Calendar option.
Select an End Date using the Calendar option.
Provide a comment in the given section.
Click the Submit option.

The selected Date column will display random dates from the selected date range.

Please Note: The Data Variance transform also provides space to add description while configuring the transformation information.
Hashing Anonymization (using Salt and Pepper technique)
This transformation using the Salt and Pepper technique is a method to protect sensitive data by introducing random noise or fake data points into a dataset while preserving its statistical properties.
Check out the illustration on the Hashing Anonymization transform.
Navigate to a dataset within the Data Preparation framework, and select a column.
Select one column that needs to be protected.
Select the Transforms tab.
Select the Hashing Anonymization (using salt & pepper technique) transform from the Anonymization category.

The Hashing Anonymization (Using the salt & pepper technique) dialog window opens.
Provide a value using the Set Values space.
Select a field using the Set Fields drop-down menu.
Select a hashing option using the Hash Option drop-down menu.
Click the Submit option.

The target column data will be displayed after applying the selected hashing option.

Please Note:
The first user-provided value (entered in the "Set Values" field) acts as the pepper.
Selected column values will act as the salt.
The hash options displayed in the UI map to the following actual hashing algorithms on the backend:
Sha1 (UI) → SHA-256 (Backend)
Sha2 (UI) → SHA-512 (Backend)
Hash (UI) → MD-5 (Backend)
MD5 (UI) → MD-5 (Backend)
Last updated