Sqoop Executer is a tool designed to efficiently transfer data between Hadoop (Hive/HDFS) and structured data stores such as relational databases (e.g., MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server).
All component configurations are classified broadly into the following sections:
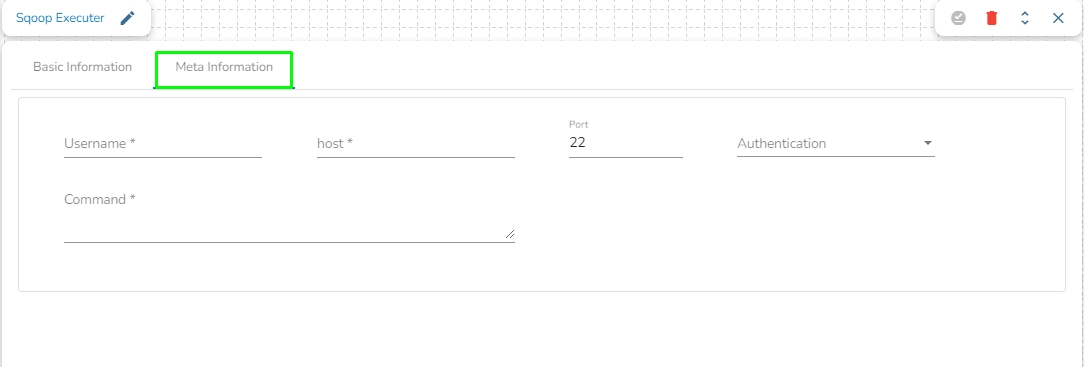
Meta Information
It is the default tab to open for the component while configuring it.
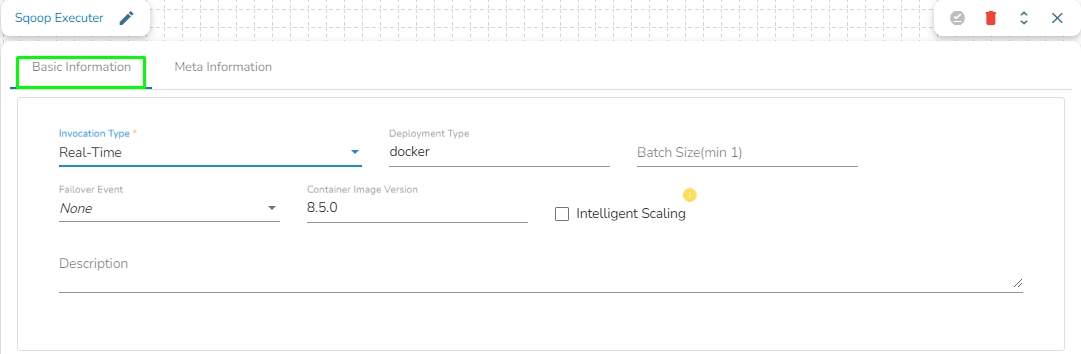
Invocation Type: Select an invocation mode out of ‘Real-Time’ or ‘Batch’ using the drop-down menu.
Deployment Type: It displays the deployment type for the reader component. This field comes pre-selected.
Container Image Version: It displays the image version for the docker container. This field comes pre-selected.
Failover Event: Select a failover Event from the drop-down menu.
Batch Size (min 10): Provide the maximum number of records to be processed in one execution cycle (Min limit for this field is 10).
Username: Enter the username for connecting to a relational database.
Host: Provide a host or IP address of the machine where your relational database server is running.
Port: Provide a Port number (the default number for these fields is 22).
Authentication: Select an authentication type from the drop-down:
Password: Enter the password.
PEM/PPK File: choose a file and provide the file name if the user selects this authentication option.
Command: Enter the relevant Sqoop command. In Apache Sqoop, a command is a specific action or operation that you perform using the Sqoop tool. Sqoop provides a set of commands to facilitate the transfer of data between Hadoop (or more generally, a Hadoop ecosystem component) and a relational database. These commands are used in Sqoop command-line operations to interact with databases, import data, export data, and perform various data transfer tasks.
Some of the common Sqoop commands include:
Import command: This command is used to import data from a relational database into Hadoop. You can specify source and target tables, database connection details, and various import options.
Export Command: This command is used to export data from Hadoop to a relational database. You can specify source and target tables, database connection details, and export options.
Eval Command: This command allows you to evaluate SQL queries and expressions without importing or exporting data. It's useful for testing SQL queries before running import/export commands.
List Databases Command: This command lists the available databases on the source database server.